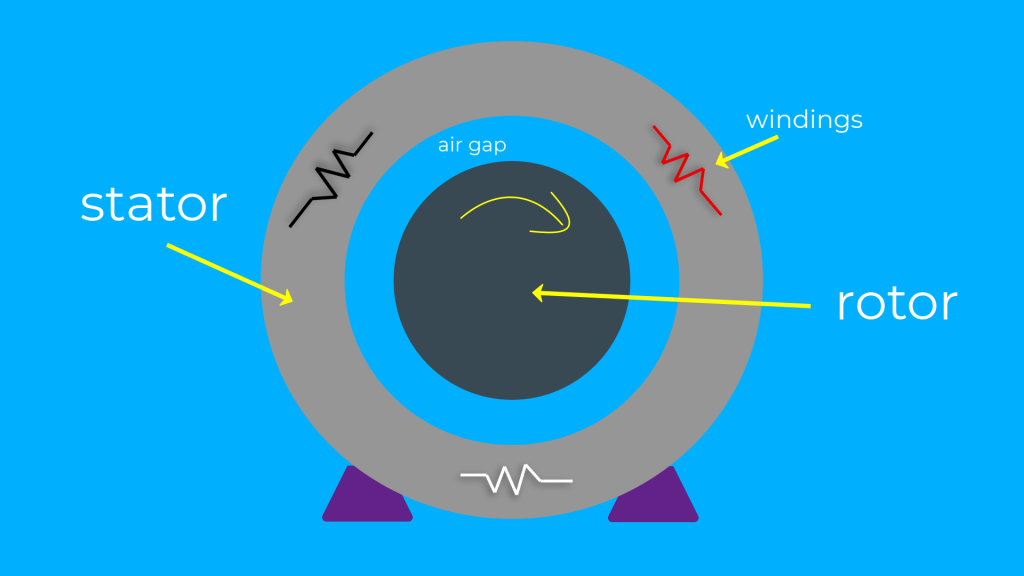
A 3-phase induction motor is a 3 phase motor that operates on electromagnetic induction. The outer part of the motor is called the stator and the inner part of the motor is called the rotor (this is the part that spins). There is no physical electrical connection between the stator and the rotor across the air gap, the spinning force is exerted on the rotor via electromagnetism.
How It Works
When power is applied to the windings of the stator, it produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field spins around and around the stator, but the stator actually stays stationary. It is only the magnetic field that circles around the stator.
Due to the rotating magnetic field being produced in the stator there is also a magnetic field being produced in the rotor (via electromagnetic induction). This is why this type of motor is called an induction motor.
The force of the rotating magnetic field in the stator pushing against the magnetic field in the rotor causes the rotor to spin. Like when 2 opposing magnets are placed together and they push each other apart.
To Recap
A 3 phase induction motor creates a rotating magnetic field in the stator when power is applied to it. A magnetic field is also produced in the rotor via electromagnetic induction. These 2 magnetic fields create a force against each other that causes the rotor to physically spin.
Learn more
Fundamentals of Electrical Controls
3 Phase Motor Control Bootcamp
Learn Variable Frequency Drives
